VxLAN: Use Layer 3 transport to carry layer 2 data. Any servers connected on different broadcast domain can talk to each other as if they are on same link.VXLAN is a MAC-in-IP/UDP encapsulation type, adding a total of 50 bytes to the original packet post-encapsulation. This is not just a single header, but multiple headers added to the original packet—this includes a VXLAN header, a UDP header, an IP header, and an Ethernet header.
VxLAN frame: outer Mac + outer IP + UDP + VxLAN + original frame ( DMAC + SMAC + Ether Type + Payload + CRC). outer MAC(14 bytes) + outer IP(10 bytes) + outer UDP(8 bytes) + VxLAN (8 bytes) = 50 bytes of extra bytes.
UDP destination port is 4789.


VxLAN header: Flags + RES + VNI(24 bits) + RES
VTEP: Switches and routers which participate in VxLAN has a special interface called VTEP. The VTEP provides connection between overlay and underlay. Each VTEP has IP address in the underlay network and VTEP also has one or more VNIs. VTEP does encapsulation and decapsulation. VTEP is usually the loopback address.
VNI: VxLAN Network Identifier. Replaces VLAN ID. It’s mapping between VLAN and VxLAN.
VxLAN segment: The resulting layer2 overlay network. The VLAN number doesn’t matter anymore. If you ARP, who all can receive it ? All those are in same VxLAN segment.
VxLAN Gateway: Device that forwards traffic between VxLANs. Can be both layer 2 or layer 3 forwarding.
NVE: Network Virtualization Edge. Logical representation of the VTEP. NVE is the tunnel interface.

VXLAN Flood and Learn (F&L)
One alternative to IP multicast for handling multidestination traffic in a VXLAN environment is to use ingress replication (IR), or head-end replication.
With IR, every VTEP must be aware of other VTEPs that have membership in a given VNI. The source VTEP generates ncopies for every multidestination frame, with each destined to other VTEPs that have membership in the corresponding VNI.
VXLAN BGP EVPN
We use BGP EVPN as control plane instead of flood-and-learn or multicast.
EVPN is an address-family within BGP (AFI: 25, SAFI: 70), and provides a control-plane to enable L2VPN and L3VPN services, as well as additional features such as Active/Active L2VPN Multihoming.
The EVPN control-plane enables VTEPs to signal to all other VTEPs which VNIs they are interested in receiving BUM traffic for. This removes the need for manual intervention relating to BUM traffic distribution. Additionally, EVPN will enable VTEPs to proactively learn information about endpoints within the environment, including:
• MAC Address,IP Address (/32 Host Route),Layer2 VNI (VLAN) Membership,Layer3 VNI (VRF) Membership,Which VTEP the endpoint resides behind,Mobility tracking number (If endpoint moves behind different VTEPs)
All the information above, and more, is advertised via BGP to all other VTEPs as soon as a frame/packet from an endpoint is seen by a VTEP.
Finally, EVPN also allows VTEPs to originate native IPv4 Unicast Prefixes, and signal to other VTEPs, via the L3VNI, which VRF (L3VPN) the IP prefix is a member of.
In nutshell, the EVPN address family allows the host MAC, IP, network, VRF, and VTEP information to be carried over MP-BGP. In this way, as long as a VTEP learns about a host behind it (via ARP/ND/DHCP etc.), BGP EVPN distributes and provides this information to all other BGP EVPN–speaking VTEPs within the network
| route-type | Name | Purpose |
| 2 | MAC-IP | Layer 2 VPN: End-Host Information (MAC, IP, etc.) |
| 3 | IMET (Inclusive Multicast Ethernet Tag) | Signal desire to receive BUM traffic for a VNI |
| 5 | IP Prefix | Layer 3 VPN: IP Prefix and VRF Membership |
Route Distinguisher and route target:
The purpose of RD is to take something that is not unique, such as IP- or MAC address, and prepend an 8-byte value to it that makes it unique. There are three different formats the RD can take:
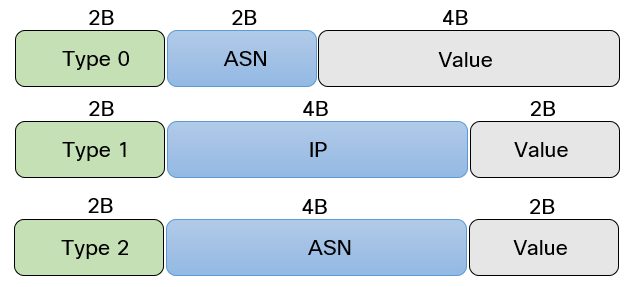
The most common format used with VXLAN is Type 1 where the 4-byte IP is the IP address of the VTEP (normally a loopback).
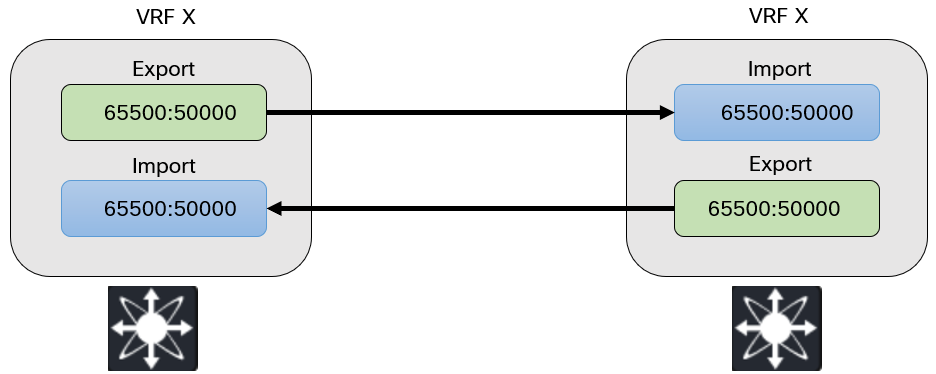
RT is an extended BGP community used to control the import and export of routes into VRFs. Think of it as a tag appended to routes where a router exporting with a RT of 65500:50000 would import a RT of 65500:50000:
EVPN terminology:
VRF:
- Layer3 Construct used to provide L3VPN services
- Enables Multi-Tenancy at Layer 3: Dedicated routing table per VRF
- Multiple VRFs can exist on a single physical device
- Inter-VRF communication (between VRFs on the same device) is not possible without additional configuration, such as route
- leaking or route-target import/export manipulation
MAC/VRF:
- Layer2 Construct used to provide L2VPN services
- Enables Multi-Tenancy at Layer 2: Dedicated control-plane and data-plane resources
- Allows for the creation of a distributed MAC Address table, where all VTEPs participating within the MAC-VRF learn the MAC addresses of all nodes within that MAC-VRF (VLAN)
- Synonymous with VLAN / Bridge Domain / Broadcast Domain
Route-Distinguisher (RD):
- Control-Plane mechanism that ensures all EVPN routes can be uniquely identified
- Globally significant value within the EVPN domain: Recommend to be unique per VRF (or MAC-VRF) on each VTEP
- It is recommended that RDs be set to a globally unique value per-VRF on each VTEP, even if the VTEP is part of an MLAG domain. A globally unique Route-Distinguisher will contribute to improved convergence time, ensure proper ECMP, and assist in validation of route origination when troubleshooting.
Route-Target:
- Control-Plane mechanism used to:
- Signal, on export (origination of EVPN route), the value that should be used by the receiving VTEP when determining two things:
- If the EVPN advertisement will be accepted
- Which VRF (or MAC-VRF) the contents of the EVPN update should be imported into
- Used, on import (receipt of an EVPN advertisement):
- to control which VRF (or MAC-VRF) to import the contents of a received EVPN update
- Signal, on export (origination of EVPN route), the value that should be used by the receiving VTEP when determining two things:
- Route-Targets are a globally significant value. In most cases, the import/export Route-Targets will match per VRF on all VTEPs. Multiple import/export Route-Targets can also be configured per VRF.
L2VNI:
- Unique per MAC-VRF
- Data-Plane mechanism, signaled via the Control-Plane
- Encoded into all EVPN Type-2 (MAC/MAC-IP) and Type-3 (IMET) updates
- VNI that is present in the VXLAN header of the packet on-the-wire when performing VXLAN bridging between VTEPs
- Signals, via the Data-Plane to the receiving VTEP, which MAC Address Table (MAC-VRF) it should perform the lookup and forwarding operation in when looking at the inner-Ethernet header
L3VNI:
- Unique per VRF
- Data-Plane mechanism, signaled via the Control-Plane
- Encoded into all EVPN Type-2 (MAC-IP) updates when operating in Symmetric IRB mode
- Encoded into all Type-5 (IP Prefix) updates
- VNI that is present in the VXLAN header of the packet on-the-wire when performing VXLAN routing between VTEPs
- Signals, via the Data-Plane to the receiving VTEP, which Routing Table (VRF) it should perform the lookup and forwarding operation in when looking at the inner-IP headers